Mars
Mars is unique across the entire solar system in that it is a terrestrial planet with an atmosphere and climate, its geology is known to be very diverse and complex (like Earth), and it appears that the climate of Mars has changed over its history (like Earth).
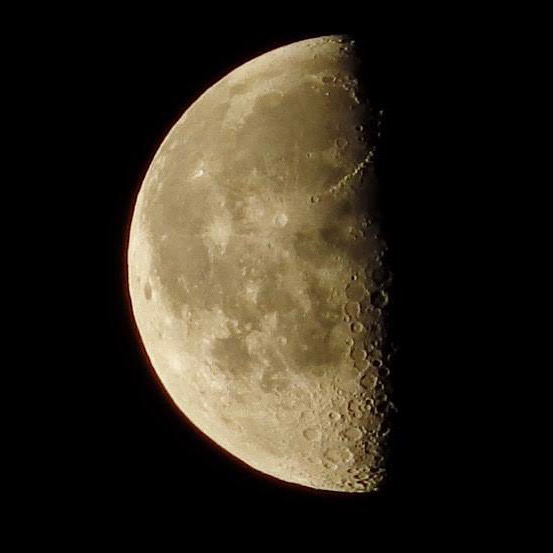


Moon
The Moon was the first place beyond Earth humans tried to reach as the Space Age began in the late 1950s. More than 100 robotic explorers from more than half a dozen nations have since sent spacecraft to the Moon. Nine crewed missions have flown to the Moon and back.
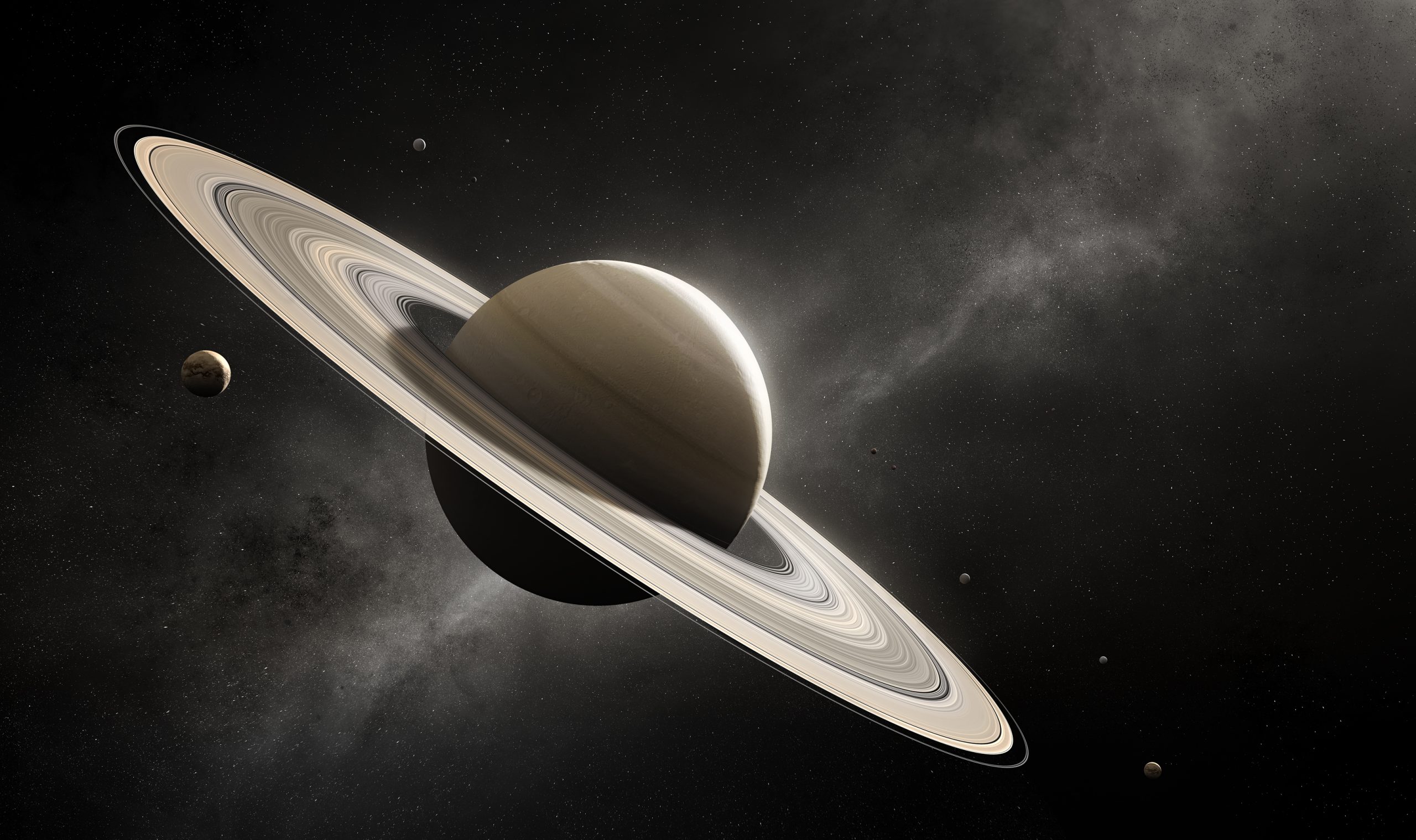
Saturn
Saturn is the sixth planet from the sun and the second-largest planet in the solar system. It has a whopping 63 official moons with another 20 awaiting confirmation of their discovery and subsequent naming. It's the farthest planet from Earth that's visible to the unaided eye, but the planet's most outstanding features — its rings — are better viewed through a telescope.

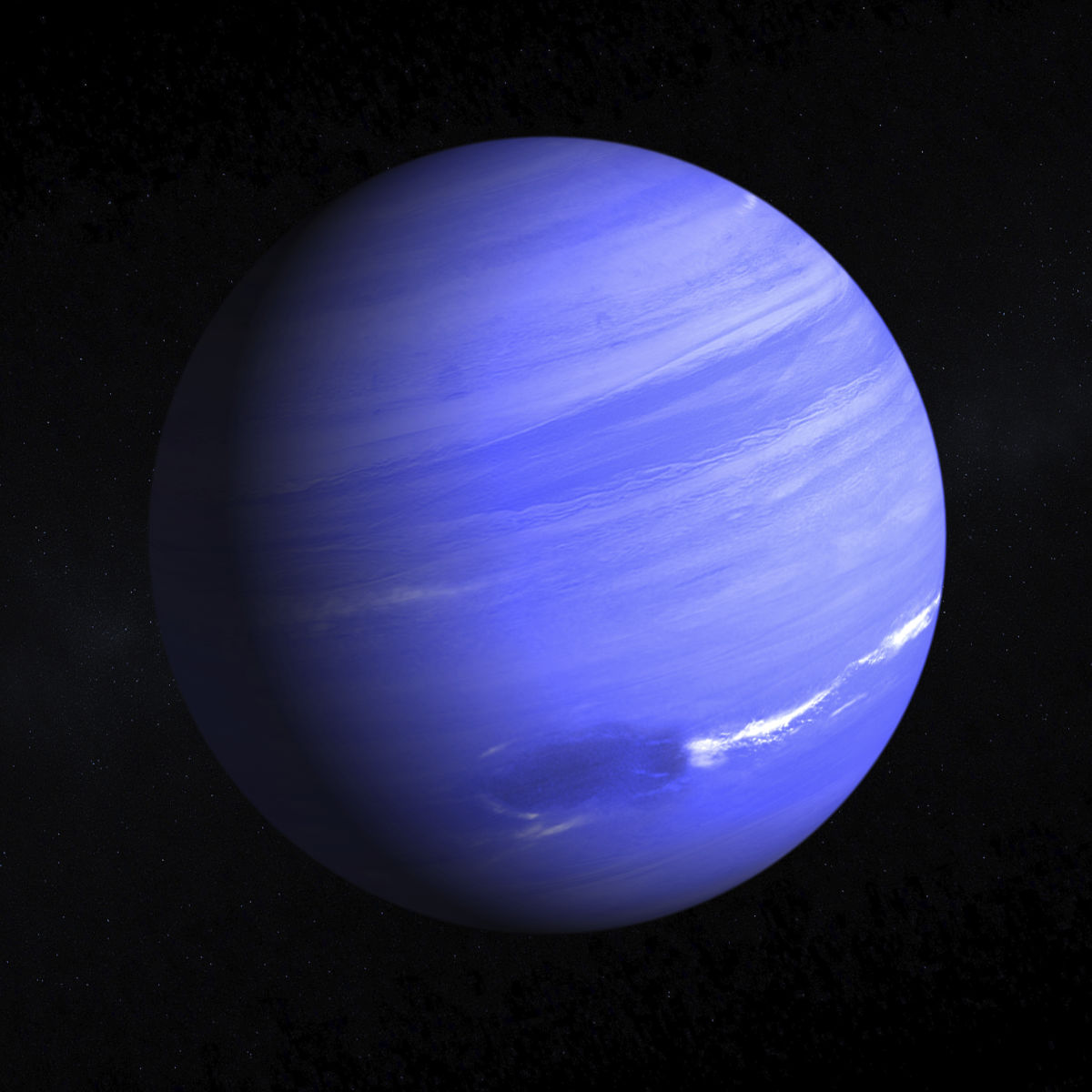
Neptune
Neptune, as we know it today, is about 30 times as far from the Sun as Earth is. This is incredibly far away, and though it is technically observable in our night's sky, it is so dim that it is lost in the "noise" of other stars and brighter celestial bodies. Since Neptune cannot readily be seen with the naked eye at night, its existence, for most of human history, was not known. In fact, up until about the 17th century, the only known celestial bodies were the Sun, Earth and the Moon (obviously), Mercury, and Venus, Mars, Jupiter, and Saturn.
